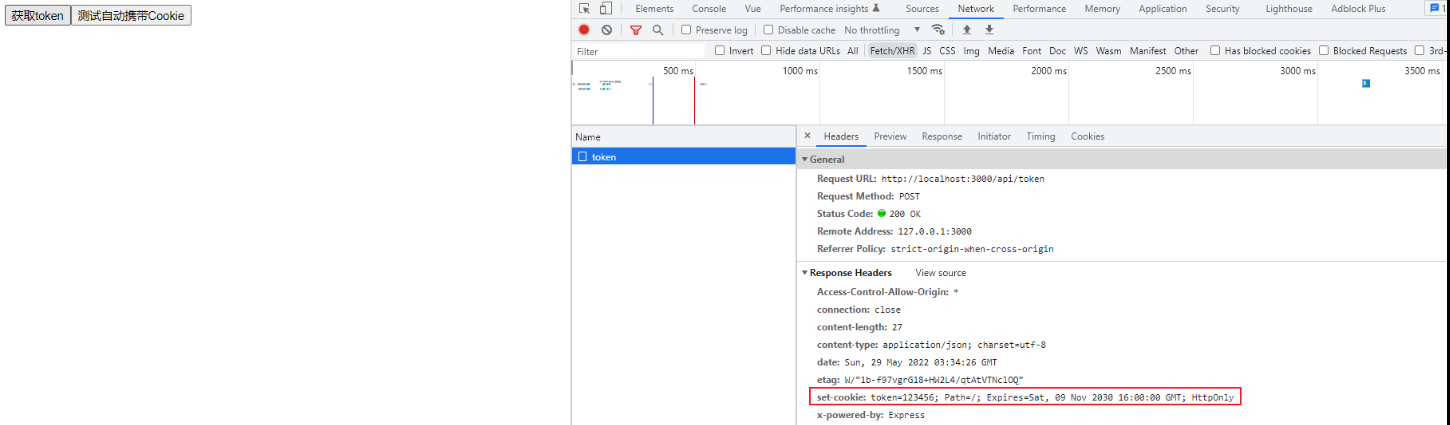
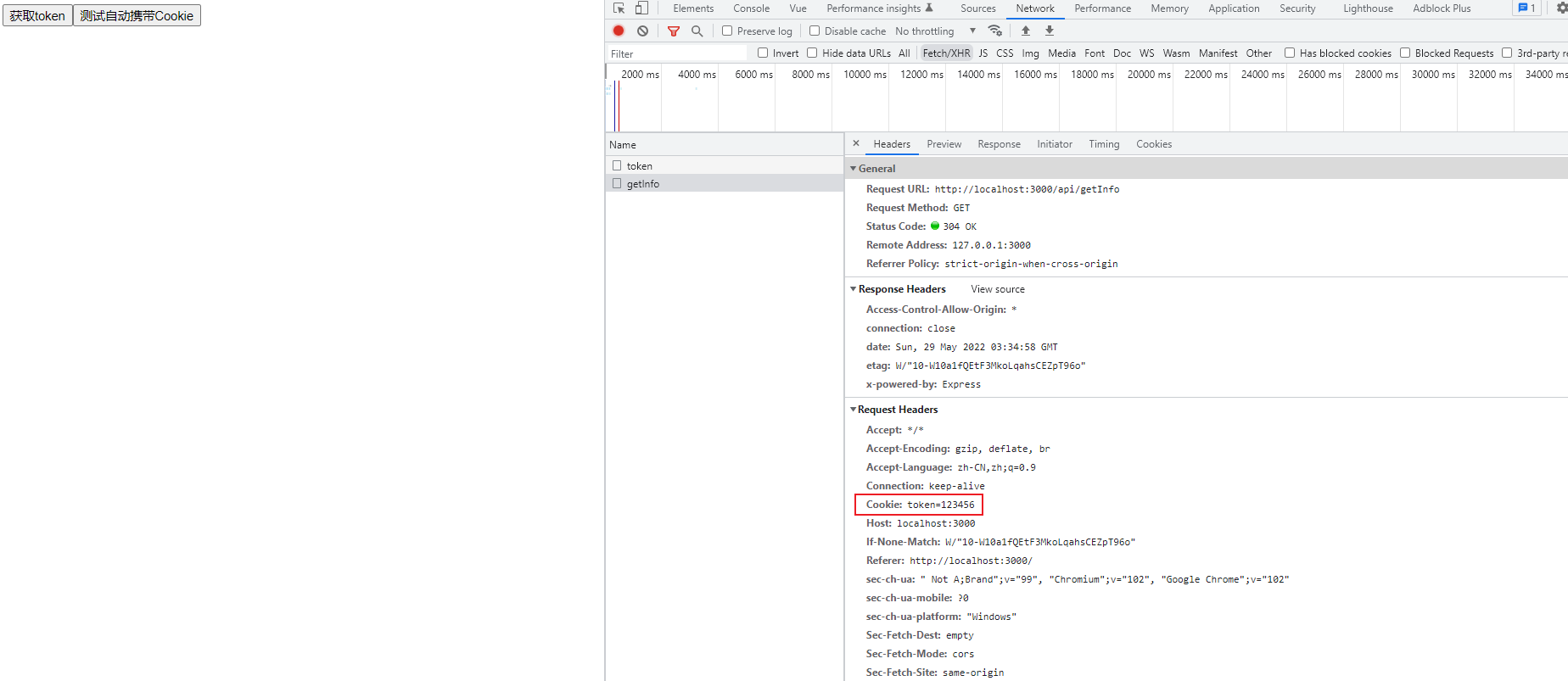
Express+FetchAPI 简单实践Cookie
本文并不是讲解Cookie在实际项目中的应用,而只是简单地实践一下,自动保存Cookie,然后后续请求自动携带Cookie,主要是通过使用刚学到的fetch API和差不多快忘记的express来实践。
Cookie 用于在客户端存储会话信息。它通过服务器响应请求时,响应头的Set-Cookie字段来设置 Cookie。Cookie 是服务端生成,保存在客户端
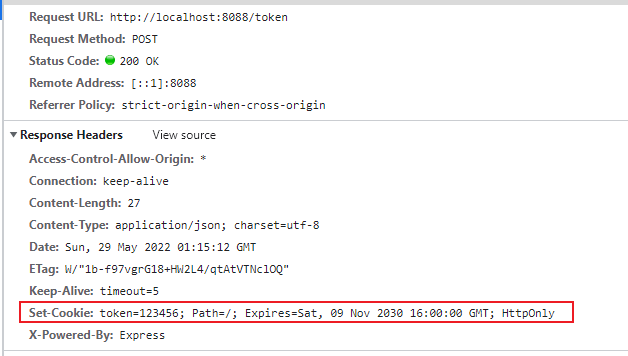
这个 HTTP 响应会设置一个名为name,值为value的 Cookie。名和值在发送时都会经过 URL 编码。
浏览器会存储这些会话信息,并且之后的每个请求都会通过请求头的Cookie字段再将它们发回服务器。
1 | |
发回给服务器的Cookie字段可用于唯一标识发送请求的客户端。
Cookie 有大小限制,一般 4K 左右。
Cookie 的构成
- 名称(
name=value):Cookie 的名称。不区分大小写,必须经过 URL 编码。 - 值(name=
value):Cookie 的值。必须经过 URL 编码 - 域(
Domain=clzczh.top):Cookie 有效的域。发送到该域名的所有请求都会包含对应的 Cookie。如果不明确设置,则默认为设置 Cookie 的域。 - 路径(
Path=/):请求 URL 中包含此路径才会携带 Cookie 发送请求。 - 过期时间(
Expires=Date):删除 Cookie 的时间戳,用于设置删除 Cookie 的时间,这个值是 GMT 格式(Wdy, DD-Mon-YYYY HH:MM:SS GMT)。当到达该时间后,就会删除 Cookie;没到达该时间时,即使关闭浏览器,Cookie 还会保留。把过期时间设置为过去的时间会立即删除 Cookie。默认只在浏览器关闭前有效 - 安全标志(
Secure):只在 HTTPS 安全连接时才可以发送 Cookie - 禁止 JS 读取 Cookie(
HttpOnly):通过 JS 脚本无法获取 Cookie,可以有效地防止XSS攻击。
Cookie 中实际发送给服务器的只有名/值对,其他部分只是告诉浏览器什么时候应该在请求中携带 Cookie 等。
Cookie 的简单实践
简单地说一下下面的代码:
- express 实现的后端服务
- 通过
app.post开启 post 接口 res.cookie设置 Cookie,第一个参数是 Cookie 名,第二个参数是 Cookie 值,第三个参数是 Cookie 的限制对象(如过期时间expires)
1 | |
前端试一下,能不能接收到Cookie。(使用 Fetch API,免装axios,实际使用和axios差不多,简单使用可查看之前的文章)
1 | |
看似万事大吉了,实际上,还是有问题的:
Cookie压根没存到客户端。
解决方案1
使用
fetch发送请求时,设置credentials为include(axios则是设置withCredentials为true),这样子跨域请求时夜会发送Cookie(也可以用来保存跨域请求响应的Cookie)1
2
3
4fetch('http://localhost:8088/token', {
method: 'post',
credentials: 'include'
})当我们设置
credentials为include时,- 我们解决跨域时的
Access-Control-Allow-Origin不应该还是通配符,而应该是具体的地址,所以后端express应该调整一下不再使用cors中间件,而是自己设置响应头 Access-Control-Allow-Credentials也应该设置为true
1
2
3
4
5
6// 使用cors中间件部分换成下面的形式
app.use(function (req, res, next) {
res.header('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', 'http://127.0.0.1:5501')
res.header('Access-Control-Allow-Credentials', 'true')
next()
})- 我们解决跨域时的
上面已经的警告已经说了:
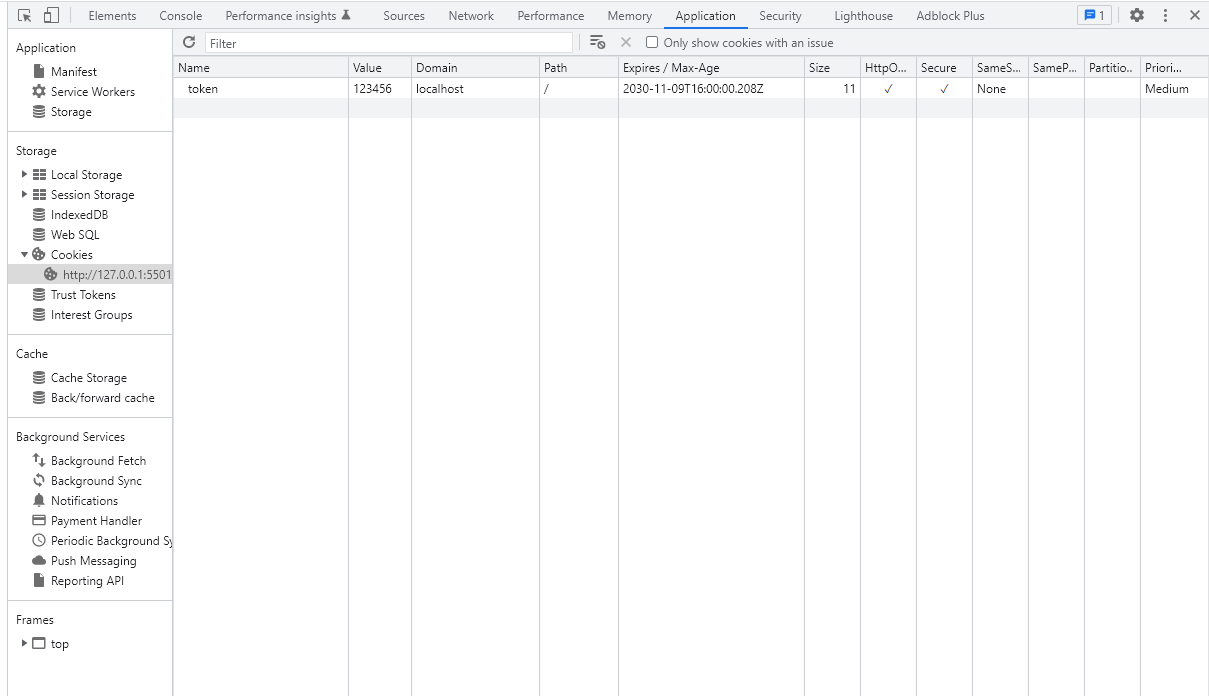
Cookie有一个SameSite属性,它默认是Lax,要求响应是对顶层导航的响应(这个顶层导航并不是很懂,有懂得小伙伴欢迎评论)。先按她的提示,设置Cookie的SameSite属性为none(安全性会下降)。有SameSite属性的话,也必须要有Secure属性1
2
3
4
5
6
7// 设置Cookie
res.cookie("token", "123456", {
httpOnly: true,
expires: new Date(2030, 10, 10),
secure: true,
sameSite: 'none'
});
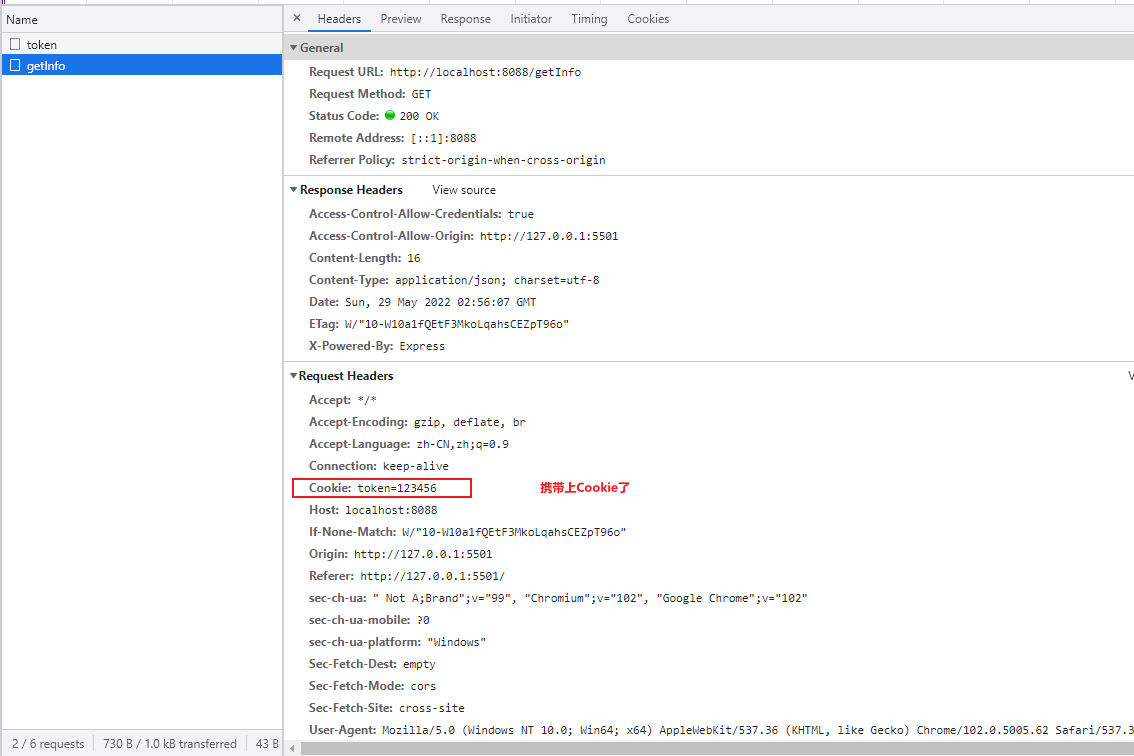
最终代码:
express:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35const express = require("express");
const cors = require("cors");
const app = express();
app.use(function (req, res, next) {
res.header('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', 'http://127.0.0.1:5501')
res.header('Access-Control-Allow-Credentials', 'true')
next()
})
app.post("/token", function (req, res) {
// 设置Cookie
res.cookie("token", "123456", {
httpOnly: true,
expires: new Date(2030, 10, 10),
secure: true,
sameSite: 'none'
});
res.status(200).json({
msg: "获取token成功",
});
});
app.get("/getInfo", function (req, res) {
res.json({
msg: "成功",
});
});
app.listen(8088, () => {
console.log("http://localhost:8088");
});html
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24<body>
<button id="btn">获取token</button>
<button id="test-btn">测试自动携带Cookie</button>
<script>
const btn = document.getElementById('btn')
btn.addEventListener('click', fetchData)
const testBtn = document.getElementById('test-btn')
testBtn.addEventListener('click', getInfo)
function fetchData() {
fetch('http://localhost:8088/token', {
method: 'post',
credentials: 'include'
})
}
function getInfo() {
fetch('http://localhost:8088/getInfo', {
credentials: 'include'
})
}
</script>
</body>
解决方案2
上面的解决方案1,非常的麻烦,还把Cookie的SameSite属性改成None了,安全性也会下降一点
实际上呢,我们有一个更简单的解决方案,只需要把他们变成不跨域就行了。
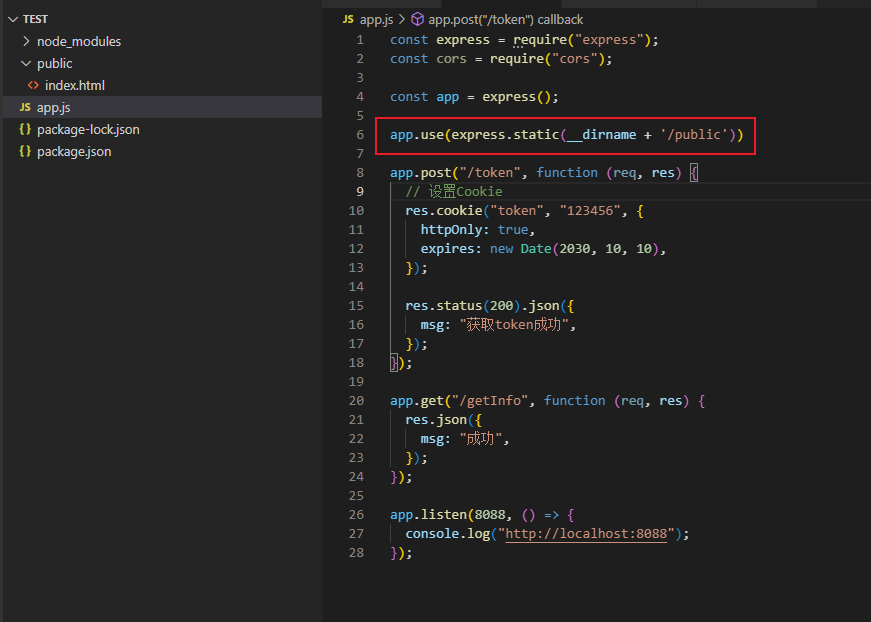
用express来测试的话,就是把之前的html代码放到express下的public文件夹里,
然后通过app.use(express.static(__dirname + '/public'))将静态文件目录设置为项目根目录+/public
然后,访问http://localhost:8088,就是我们写的html,不跨域,自然就没有解决方案1中出现的问题了.
当然,只看上面的例子的话,好像是用解决方案2的话,前后端就不能很好的分离了.其实并不是,我们可以通过nginx的代理来解决前后端的跨域问题.
可以使用Vue来简单实践代理能否解决这个保存携带Cookie问题.
首先呢?我们需要修改配置文件,实现代理.
1 | |
fetch API的请求地址就不再需要去到后端的那个接口地址了,而是变成/api即可,这样子代理就会把这个请求转发给真实服务器.
1 | |